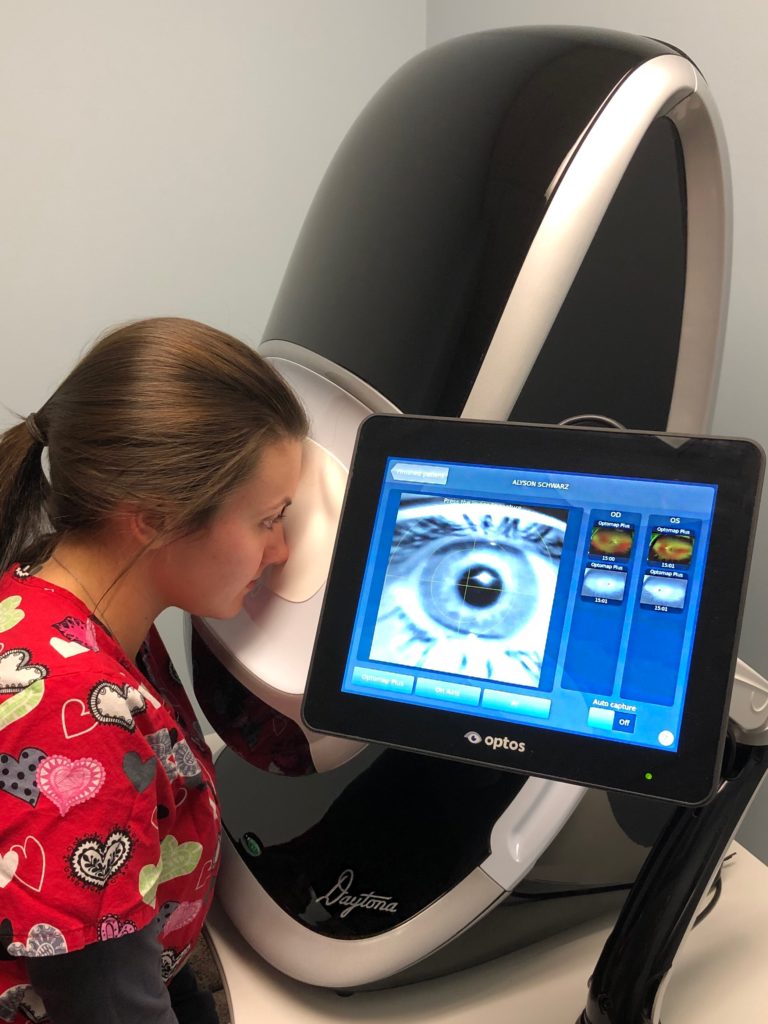
When performing the Optomap on patients we are frequently asked, “What is the purpose of this test? Do I really need this?” This article goes through some of the benefits as well as some of our most frequently asked questions. Often there are things going on in your body you are unaware of, and an Optomap can be a window to look inside and see what’s going on. We are hoping to shed some light on this portion of your exam and hope to help you understand the importance of proper eye health and preventative care.
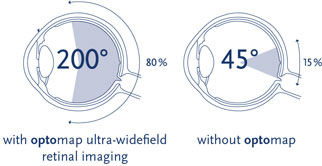
The Optomap image screenings are used to check your retina, which is located in the back of your eye. The retina is the only place in your body where the nervous system and the circulatory system can be directly seen without cutting the body open. Traditional methods to see the retina include the use of what is known as a slit lamp and/or dilation. A slit lamp is a piece of equipment that uses a narrow bright beam of light and a small mirror to see the interior of the eye. Another traditional method is dilation of the pupil. However, dilation alone is not enough for the doctor to see all the way into the eye to the retina. Dilation is used to assist the doctor when using the slit lamp, it opens the pupil when the pupil is too small to see into the back of the eye. With these traditional methods however, the doctor is only able to see 15% of the retina. With an Optomap, the doctor is able to see 80% of the retina. This is a HUGE difference, 65% more of the retina can be seen using Optomap imaging. Early signs of pathology can present in the periphery of your retina and remain undetected for a long time with traditional methods. Early detection is key and the Optomap allows the doctor to see more of the periphery and to see it sooner!! Early detection means successful treatments can be administered and can greatly reduce risk to not only sight, but many other health problems.
With an Optomap the doctor will see if your macula and retina are both healthy. They will also see floaters, retinal detachments, retinal hemorrhages, and many other eye problems. Optomap imaging is a useful tool for early detection of other health problems such as: heart disease, hypertension, cancer, and diabetes. All of these health problems and many more can be detected by monitoring your retina. Changes in your retina are seen using Optomap imaging long before you notice any changes in your vision or other physical symptoms or pain.
Optomap images are quick and painless. Nothing touches the eye itself and the image is captured in less than ½ a second. The images are taken one eye at a time. Our staff takes two pictures of each eye. The second image is taken using an auto-fluorescent setting that allows the doctors to see if there are any leaks in the blood vessels. The instrument uses a bright flash of light, similar to the flash of a camera, and internal mirrors to capture the image. The images captured are available to the doctor right away, along with a 3D animation of the eyeball. The 3D image projects your retinal image to show you exactly where everything is, exactly as it appears in your eye.
FAQ’s:
Q: Is there an age requirement? Is an Optomap safe for kids?
A: Yes, the Optomap testing process is safe for children and adults. There is no age requirement or limit. It is also non-invasive and completely painless. Many vision problems begin during early childhood so early intervention is key to preserving vision.
Q: How often should I have an Optomap performed?
A: Generally, it is recommended to be done with each routine eye exam. For a more specific recommendation, ask your doctor at your next exam and they would be happy to come up with a custom care plan for your individual case.
Q: How does this help me as a patient?
A: Optomap images can help the doctor to detect problems in a faster, more efficient, and more comfortable way. Optomap images are also kept in the patients file for future reference and/or comparisons. Having a baseline image to compare future images to is extremely beneficial to the patient, as well as the doctor, and can lead to earlier detection and intervention if a problem should arise. Early intervention is key in preventing loss of vision or other serious health issues.
Q: Will I need to be dilated and does it hurt?
A: An Optomap is not painful and only take seconds to perform. You do not need to be dilated to perform the test, however your doctor may decide dilation is still necessary.
